A 2023 research report from Wiley University Services reveals that nearly seven in 10 human resource professionals believe their organization has a skills gap. The stakes for improving employee training in an organization are high. McKinsey & Company states that improving skills can boost productivity by a whopping 40%.
Most organizations understand that artificial intelligence can play a role in closing the skills gap through rapid upskilling and reskilling. But less well-known is that the pedagogy behind AI is equally important for learning success. Improving pedagogy lets you realize the full potential of your AI investment for employee training.
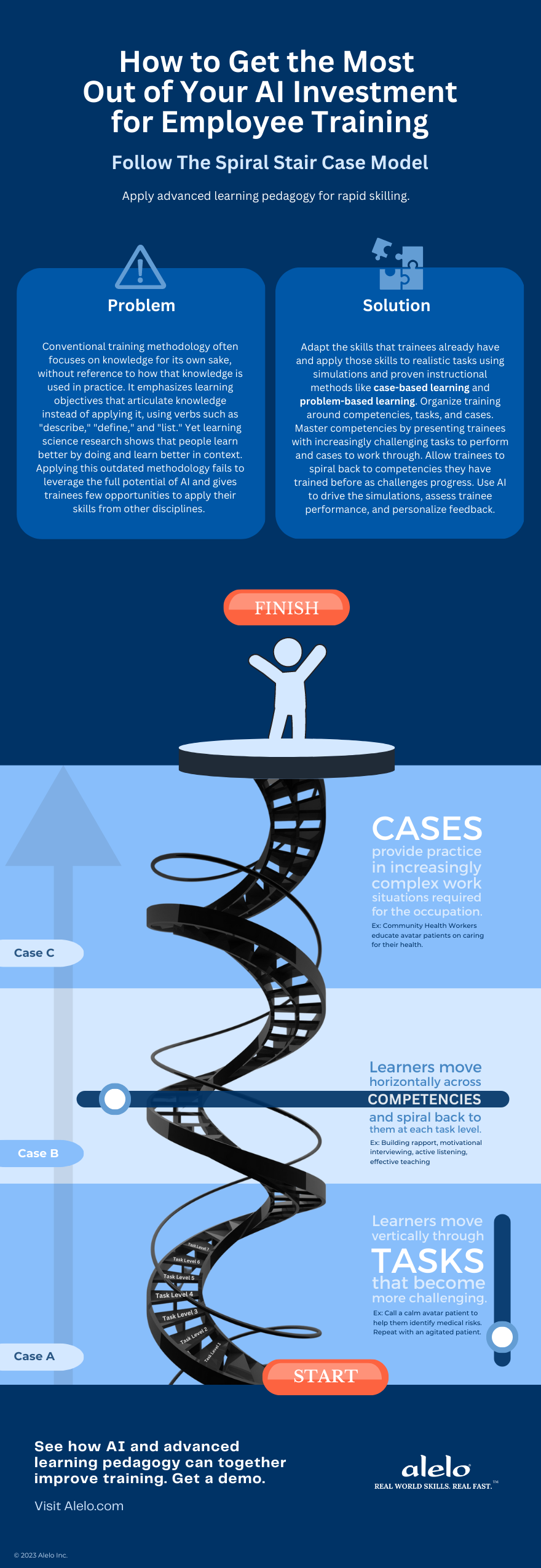
Learning science tells us that case-based learning and problem-based learning are far more effective than conventional training methodology which focuses on knowledge instead of how knowledge is used. This infographic shows how Alelo applies learning science concepts using its Spiral-Stair-Case-Model to maximize learning delivered with AI.
EMBED CODE
<iframe src=”https://www.alelo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/maximize-ai-investment-in-employee-training.png” title=”How to Get the Most out of Your AI Investment for Employee Training” width=880px height=2550px></iframe>
Summarizing the Spiral-Stair-Case-Model
To maximize your AI investment for employee training, organize learning around cases, competencies, and tasks.
- CASES are specific situations in which workers must perform tasks as part of their occupation. In each case, the trainee must employ one or more competencies. Successful completion of the task provides evidence that the trainee has mastered the competencies. An example of a case is a Community Health Worker educating an avatar patient on caring for their health.
- COMPETENCIES are the knowledge, skills, abilities, and behaviors that contribute to individual and organizational performance. They can be broad and encompass multiple sub competencies. In our Community Health Worker example, competencies include building rapport, motivational interviewing, active listening, and effective teaching.
- TASKS are activities related to the completion of a person’s work or job. They can be complex and subsume multiple subtasks. Example: a Community Health Worker performs the task of calling a calm avatar patient to help them identify medical risks, then repeats the task with an agitated patient.
Learning in this model proceeds in a series of steps, moving laterally (from one competency to the next) and vertically (to progressively higher skill levels and tasks). As trainees progress, they spiral back to competencies they have trained before, but are presented with more challenging cases to further improve their skills. In this way, learning progresses rapidly in an ever-ascending spiral.
By combining AI with science-backed pedagogy, you can scale employee learning rapidly and effectively.
Read a case study in the International Journal of Advanced Corporate Learning to see how Alelo applied the Spiral-Stair-Case-Model to train Community Health Workers in half the time for the XPRIZE Rapid Reskilling competition.


